This article is part of a series; click here to read Part 1.
The fundamental risk for retirement is unknown longevity, which is summarized in the question, how long will your retirement plan need to generate income? It is the risk of running out of assets before running out of time. The length of retirement could be much shorter or longer than the statistical life expectancy. A long life is wonderful, but it is also costlier and a bigger drain on resources. Half of the population will outlive their statistical life expectancy, and that number is only increasing as scientific progress increases the number of years we can expect to live. For some retirees, the fear of outliving resources may exceed the fear of death. This can create a paralyzing effect on retirement spending.
Click here to download our resource, How Long Can Retirees Expect to Live Once They Hit 65?
When determining longevity, it may seem natural to base calculations on the aggregate US population, but clear socioeconomic differences have been identified in mortality rates. Higher income and wealth levels and more education each correlate with longer lifespans. This may not be a matter of causation (i.e., more income and education cause people to live longer), but perhaps an underlying characteristic leads some people to have a more long-term focus, and that, in turn, may lead them to seek more education and practice better health habits. The very fact that you are reading this somewhat technical tome on retirement income suggests you probably have a longer-term focus and can expect to live longer than the average person. In this case, mortality data based on population-wide averages will underestimate your longevity.
Retirement Researcher
Not everyone will live longer, as unfortunate accidents and illnesses will inevitably befall some along the way. But in a statistical sense, my average reader will live longer than the average person.
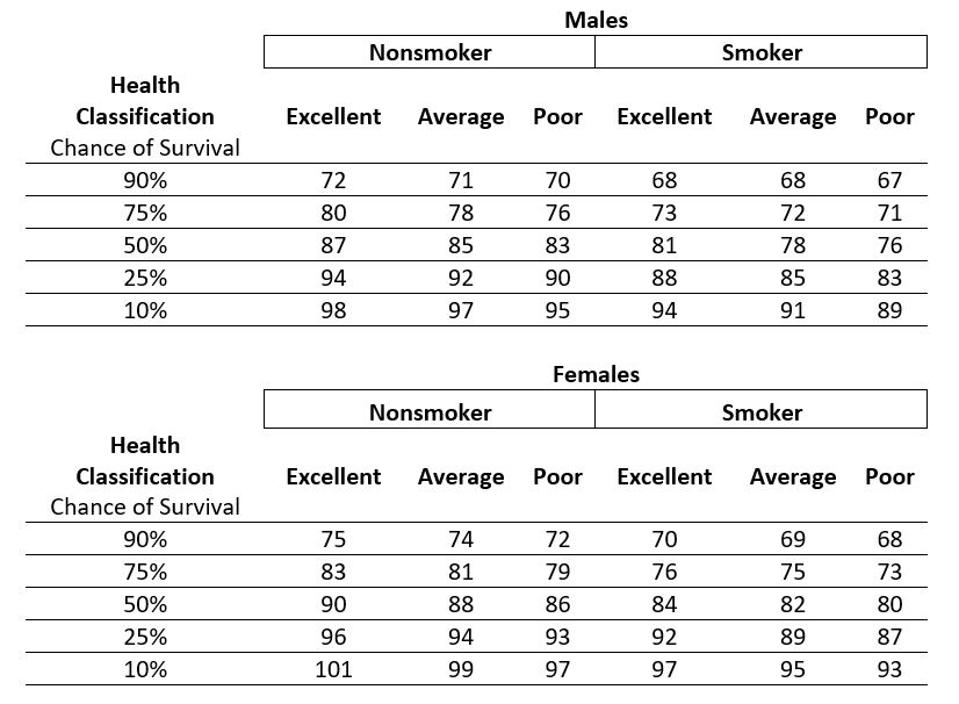
The American Academy of Actuaries and the Society of Actuaries created the Longevity Illustrator to help users develop personalized estimates for their longevity based on a few questions about age, gender, smoking status, and an overall assessment of health. It is a free and simple-to-use resource. Exhibit 1.1 provides its output for sixty-five-year-old males and females based on their health assessment and smoking status.
Exhibit 1.1
Planning Ages for Sixty-Five-Year-Olds from the Longevity Illustrator
Retirement Researcher
Source: The Longevity Illustrator
In a probability-based world, the available means for an individual to manage longevity risk is to choose a conservative planning horizon for which there is a sufficiently low probability to outlive. This will require spending less so that available assets can be drawn out for a longer period of time. The probability of surviving to advanced ages is low. Individuals must determine how low a level of spending they are willing to accept today in their effort to plan for a longer life and better ensure that they will not deplete their assets before death.
For example, a nonsmoking sixty-five-year-old female in average health who is willing to accept a 10 percent chance for outliving her financial plan would want her plan to work to age ninety-nine. For a male with the same characteristics, age ninety-seven corresponds to accepting the same amount of longevity risk.
In 1994, William Bengen chose thirty years as a conservative planning horizon for a sixty-five-year-old couple when he discussed sustainable retirement spending. But as mortality improves over time, this planning horizon is becoming less conservative, especially for nonsmokers in reasonable health.
The Society of Actuaries (SOA) also produced the 2012 Individual Annuity Mortality tables that I think will appropriately reflect the situation for my readers. Compared to the Longevity Illustrator numbers shown in Exhibit 1.1, the individual annuity mortality table corresponds with data for nonsmokers in average to good health. And this data set provides mortality rates at all ages, making it useful for supporting other annuity calculations. This mortality data is specifically for annuity purchasers who tend to live longer than average. For instance, those with significant illnesses tend to avoid buying annuities. The data also reflects estimates for future mortality improvements and is not based only on the situation in one year.
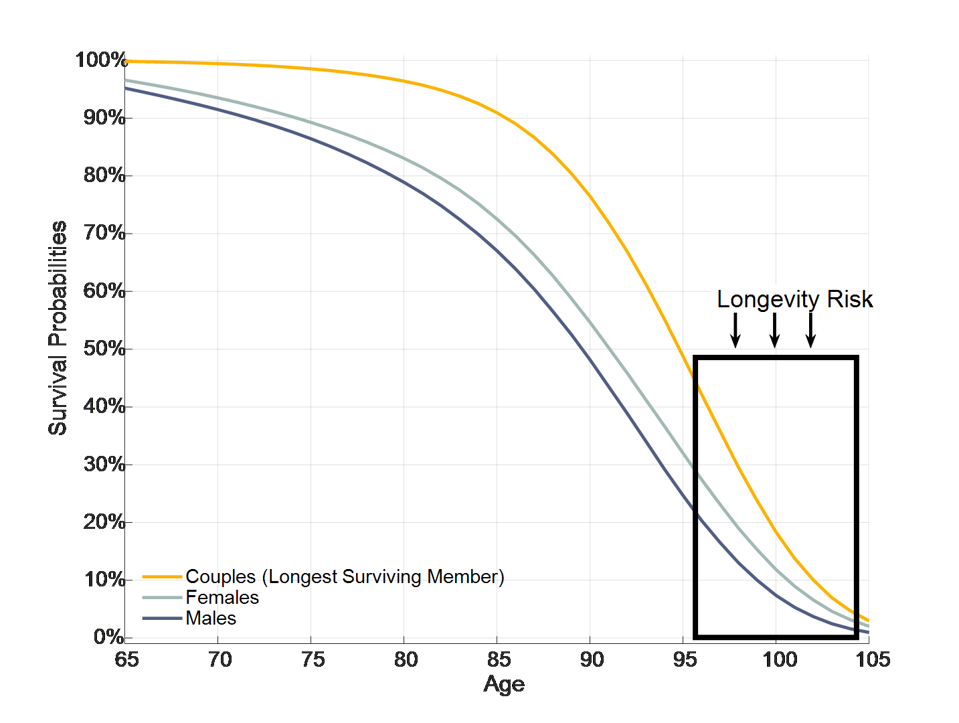
Exhibit 1.2 uses this data with mortality improvements projected for a starting year of 2019 to illustrate longevity risk by showing the probability of survival to different ages beyond sixty-five. It also shows outcomes for a couple’s joint longevity. With retirement planning, the trouble is knowing what age to plan for, as this distribution of potential retirement lengths is quite wide. With this data, the probability of a sixty-five-year-old reaching age ninety-five is 23 percent for males, 30 percent for females, and 46 percent for at least one member of an opposite-gender couple. For a couple, thirty years is getting close to being the life expectancy for its longest living member. The probability of outliving a thirty-year time horizon is not insignificant. Longevity risk is the risk of living longer than anticipated and not having the resources to sustain spending for a longer lifetime. It is reflected in the exhibit as if one builds a plan to work through age ninety-five but then lives past this age.
Exhibit 1.2
The Probability of Survival from Age Sixty-Five and the Longevity Risk for a Planning Age of Ninety-Five
Retirement Researcher
Source: Own calculations for Society of Actuaries 2012 Individual Annuitant Tables with improvements through 2019.
This is an excerpt from Wade Pfau’s book, Safety-First Retirement Planning: An Integrated Approach for a Worry-Free Retirement. (The Retirement Researcher’s Guide Series), available now on Amazon.
