African-Americans are More Likely To Fall Ill and Die From Covid-19 Than Whites
Getty
Amid massive nationwide protests over the police killings of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Tony McDade and others, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s latest data shows massive racial disparities in the ongoing coronavirus pandemic. The share of African-Americans among all people with the novel virus is almost twice as high as their population share. Thus continues the disparate trend that has characterized this pandemic, whereby African-Americans become infected and die from Covid-19 at higher rates than whites. These disparities are the outcomes of several varied instances of systemic racism that regularly and systematically devalue and treat Black lives as disposable.
A long and well-documented history of systematic discrimination against Black people regularly leads to worse underlying health conditions for African-Americans that make it more likely they become severely ill during this pandemic and die from the disease. For decades, scientists have studied the various factors that contribute to the harm that African-Americans are now suffering. None of this is a mystery. It is high time that these insights translate into sustained policy actions to prevent the unnecessary suffering and deaths among African-Americans.
Most importantly, policy steps need to be race conscious to pay a lot more attention to the systematic issues that lead to greater deaths among African-Americans. Race neutral policies that instead reflect and retain the underlying disparities will only ensure that Black patients will continue to die in larger numbers than whites.
African-Americans have worse underlying health conditions in large part because they are regularly more exposed to health hazards than is the case for whites. These health disparities are neither a reflection of genetic or behavioral differences, but of policies that often harm Black communities. Several books have documented that Black families often live in communities with worse air and water quality than white families do. The fact that residents of Flint, Michigan, a majority Black city, continue to live with high levels of lead in the water for several years is not an exception, but the rule. Black children are also more likely to suffer from asthma due to persistent housing segregation, which restricts tens of millions of Black families to overcrowded substandard housing with higher rates of exposure to vehicular pollution, fecal matter from rodent and insect infestations, and mold spores. The cumulative effects of persistent and widespread environmental health hazards such as these contribute to massive racial differences in underlying health conditions, making it more likely that Black people get sick and die from the new virus.
There is also increasing evidence that racist comments and aggressive and often violent racist actions have a cumulative negative effect on African-Americans and others at the receiving end from these aggressions. Obviously, violent physical attacks against Black people, which have a long, sad and continuing tradition in the United States, directly affect their health and well-being. But, derogatory comments and discriminatory actions such as being denied a promotion or being followed at the grocery store result in higher instances of depression and anxiety. The combination of the widespread pandemic with its disproportionate effects on African-Americans with the protests over the violent death of George Floyd at the hands of Minneapolis police officers, among others, have further increased stress and anxiety levels among African-Americans from already disproportionately high levels. These mental health challenges exacerbate already widespread disparities in underlying conditions such as hypertension that make covid-19 more deadly.
A related point is the racial disparity in the criminal justice system, as has become abundantly clear during weeks of nationwide protests over police killings of Black people. African-Americans are more likely to be stopped by the police, to be arrested, to become victims of police violence and to be incarcerated than whites. These actions have obvious direct consequences on Black people’s physical health and lives. But, all of these actions result in worse physical and mental health outcomes for all African-Americans afraid of interactions with the police. More stress, anxiety and depression again increase the chances that Black patients with covid-19 will die from the disease.
Systematic societal differences don’t end there. Black families are also more likely to live in food deserts, where they no or little access to healthy food options. The lack of well-stocked supermarkets as well as restaurants with healthy menu options often leads to adverse health outcomes such as obesity and diabetes – conditions that also exacerbate the lethality of covid-19. African-Americans suffer from worse health because of a system that undervalues their lives on a daily basis.
African-Americans are not only at higher risks of falling ill and dying from the novel coronavirus than whites. They are also at higher risks of catching the virus in the first place. Black workers are steered towards service industries and occupations that make social distancing harder and put Black families’ physical health at risk right now. Worse, while many of these jobs are considered essential, people doing them are not seen as essential, as Women’s Institute for Science, Equity and Race’s president Rhonda Sharpe points out, since they are often forced to work in hazardous conditions without proper protective equipment.
Things only get worse when African-Americans actually become ill. For one, they often find fewer health care resources than whites do. Hospitals in Black neighborhoods have been more likely to close than in white neighborhoods, leaving African-Americans with fewer options to seek care when they fall ill. And, health care providers let their own biases come into play as when they rely, for examples, on stereotypes of Black patients’ health tolerance and provide less care than for whites. Black patients do not have the same chance as white people of getting better when sick.
Occupational steering also means fewer financial resources in case African-Americans fall ill. Black workers get paid less, are less likely to have health insurance and have less wealth, including emergency savings, than whites. This means African-Americans end up paying more for health care because of worse health insurance, but they have less money to pay for such care because of lower wages and fewer savings. African-Americans, for instance, are more likely to end up with medical debt in case of an unexpected health emergency than is the case for whites (see figure below).
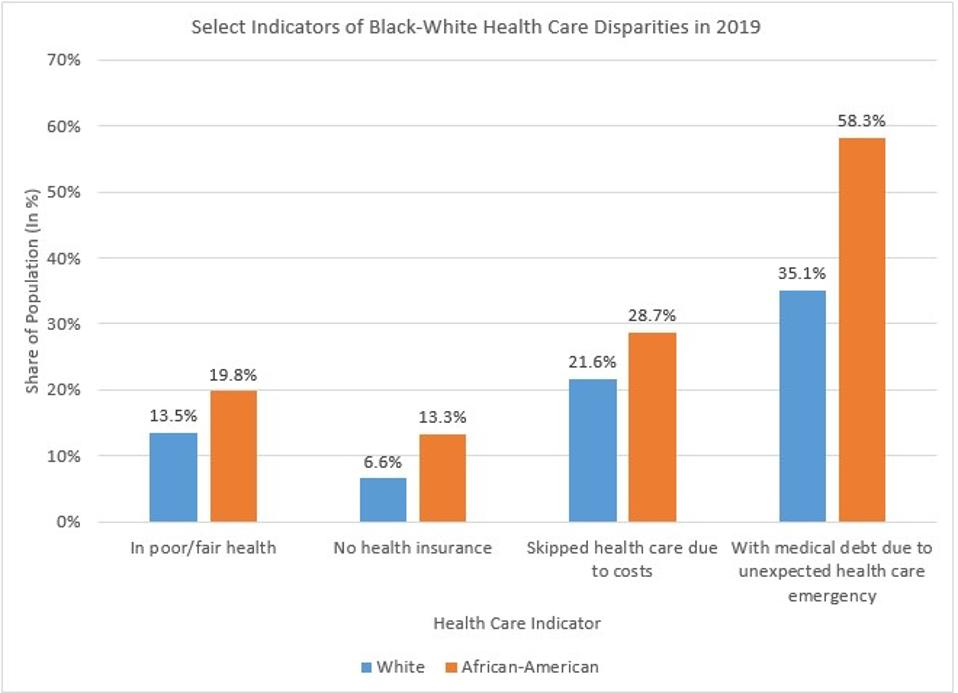
African-Americans Are At Greater Physical and Financial Risk In The U.S. Health Care System.
Calculations Based on Federal Reserve, Survey of Household Economics And Decisionmaking
Many African-Americans also harbor distrust of the medical profession for good reason as a result of a long history of abuse by doctors and researchers. One of the starkest examples of such abuse is the Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in Negro Men, whereby Black men infected with syphilis were tested but never told why they were tested nor provided available treatment for the disease. The study lasted for 40 years and was eventually shut down after public outcry in the early 1970s. Recently, Marcella Alsan from Stanford University and Marianne Wanamaker from the University of Tennessee concluded that the resulting distrust of health care providers among African-American men shortened their life expectancy significantly. Many understandably did not seek preventive care as they did not trust a system that had treated them as disposable for decades.
Less health care utilization due to, among other things, lack of trust feeds back into higher costs for health care and greater denials of care in health insurance algorithms. Because algorithms don’t identify the underlying institutional structures that result in African-Americans ending up with less medical care, Black patients look healthier in the data than whites simply because they are denied care more often. Health insurance algorithms then cover less health care to them, for instance, by making it less likely that Black patients are identified for additional care. The insidious consequence of systemic bias in health care is that this bias is perpetuated in the way health insurance companies decide who gets what kind of care.
These are just some of the facts that put African-Americans at greater risks during the current pandemic. Black people suffer from more underlying conditions, less access to quality health care and greater financial risks when getting sick. The U.S. has created a system that puts Black people’s health and lives at risk on a daily basis. This persistent, systemic racism goes well beyond widely publicized violent and often deadly incidences such as police killings. The devaluation of Black lives is built into many daily routines. Making Black lives matter will mean addressing all of these facets of systemic devaluation and dehumanization of African-Americans’ lives.
