For business owners, the Roth IRA may be a very attractive savings vehicle.
getty
Roth IRAs and 401(k)s (called DRAC, or Designated Roth Account) are common wealth-accumulation tools. There are multiple ways to utilize a Roth, and they offer significant financial planning opportunities, notably the elimination of Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) friction (‘tax friction’) and the protracted compounding period of the joint lives of the Roth owners plus 10 years, thanks to the SECURE Act. Roths possess some primary characteristics:
· All qualified earnings are tax-free
· There are no Required Minimum Distributions (RMD) to the owners (if the Roth 401(k) is rolled into a Roth IRA)
· An inherited Roth (for inheritances after 2019) may be withdrawn up to 10 years after the death of the owner
There are two primary ways to fund a Roth, either by contributing (e.g., contributory Roth IRAs, back-door Roth or DRAC) or by converting an existing RIA (or in some cases, 401(k) to a Roth by paying the taxes on the conversion). These attributes can provide significant advantages, particularly if the tax rate at the time of conversion is lower than the prospective tax rate at the time of distribution.
Business owner with 2020 losses. Suppose our conversion candidate is a 45-year-old business owner who had a bad 2020 (no surprise here). Let suppose Randy and Gail have a restaurant that was limited in 2020 and they generated a loss of $100,000. They could theoretically convert $124,800 with no taxes (although they would use up their NOL tax benefits). What would a $124,800 conversion look like for a 45-year-old?
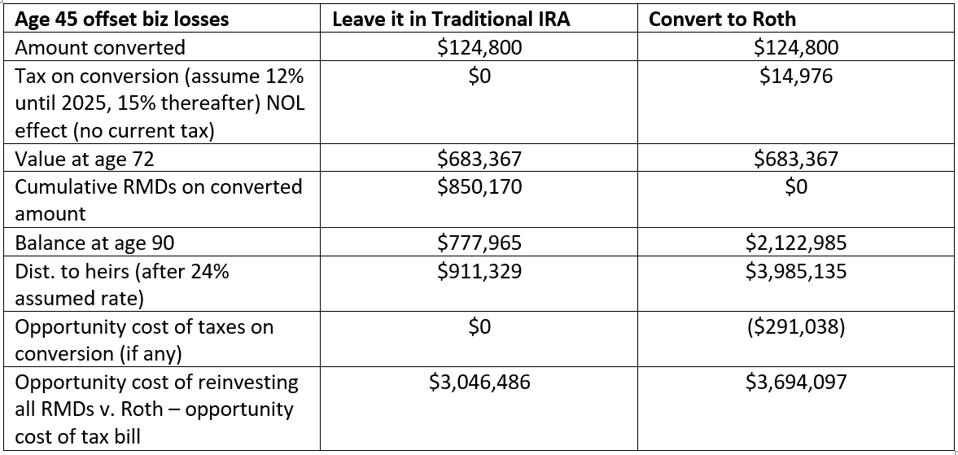
Comparison is key, the numbers don’t lie.
Leon LaBrecque
MORE FOR YOU
In addition, some business owners may have gotten a Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) Loan, which provided additional funds.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Biz-Owner Conversion: Get a QBI deduction on the Roth. Here is a big one. Business owners with ‘pass-through’ entities can use a ‘Qualified Business Income’ (QBI) deduction of 20% of the QBI. Thus, a business owner with $100,000 of QBI can get a $20,000 deduction. Some business owners in ‘Specified Service Trade or Business’ (SSTB) like doctors, lawyers, actors, and CPAs can use the QBI deduction on pass-through income as well, but have a limit on the QBI deductions based on their taxable incomes ($326,600 for married filing jointly and $163,300 for others). Using a Roth 401(k) instead of pretax 401(k) can create a deduction instead of a deferral. In addition, the QBI deduction expires at the end of 2025. A married pair of veterinarians making $270,000 of QBI are in about a 19.2% rate. In 2026, they’ll go back to 33% (or more). So, if our 50-year old couple makes Roth 401(k) (DRAC) contributions of $26,000 ($52,000 total) each for years 2020 through 2025, and they made 6.50% on their investments, here is what we might expect to see:
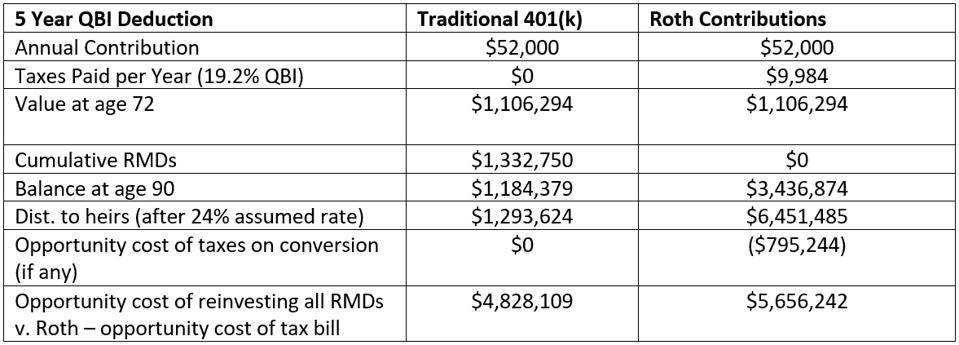
If you’re a business owner, your QBI deduction could be put to good use with a Roth IRA.
Leon LaBrecque
By saving into the DRAC over the next 5 years they are able to provide their heirs with over $800,000 in additional assets. What do they do in 2026? Go back to saving on a pre-tax basis. Business owners with QBI should carefully consider whether the advantage of the QBI deduction would make a Roth strategy more effective in their circumstances.
Bottom Line: Business owners need to sharpen their pencils (or polish their spreadsheets) as we close out 2020, but these two ideas can help make lemonade from lemons. If you want more information, download our free e-book on IRAs, updated for 2020. As always. I’ll try to answer questions at llabrecque@sequoia-fiancial.com.
